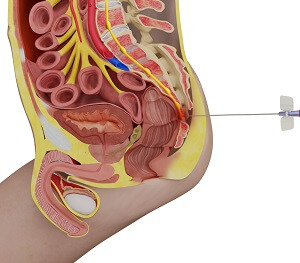
A ganglion impar block is used in the management of chronic pelvic or rectal pain. Ganglion impar refers to a group of nerve cells located close to the coccyx. The coccyx, also known as tail bone, is located at the lower end of the spine. The coccyx consists of three or more small bones fused together.
A ganglion impar block can be used for diagnostic as well as therapeutic purposes. In a diagnostic block, a contrast agent along with a local anesthetic is used to determine the source of pain while in a therapeutic block, a contrast agent, local anesthetic, and steroid are collectively used to reduce the pain and inflammation.
A ganglion impar block is not recommended in individuals with flu, fever, high blood pressure, active infections and those on blood thinning medications.
Procedure
The procedure usually takes about 10 to 15 minutes. The patient lies on their stomach, on the operating table. Your physician will clean the intended site with iodine and cover it with a sterile drape. A local anesthetic is then used to numb the skin. Under X-ray (fluoroscopy) guidance, a small amount of contrast dye is injected to confirm the positioning of the needle. This is followed by the administration of a local anesthetic and steroid mix, through the needle. The needle is then removed and a dressing is used to cover the injection site.
If you are allergic to the contrast agent, inform your doctor before the procedure.
After the procedure
You may need a companion to drive you home after the procedure. You can resume your daily routine activities but avoid swimming, or soaking in a tub, pool or Jacuzzi on the day of your procedure. You may experience some tenderness around the injection site for which ice can be applied to relieve the discomfort.
Risks
Risks and complications of ganglion impar blocks are rare but can include infection, bleeding, pain, and allergic reaction to the anesthetic or steroid. You may experience numbness and increased pain for a few days after the procedure. In diabetics, steroids may be associated with a temporary rise in blood sugar level.

